Arthritis

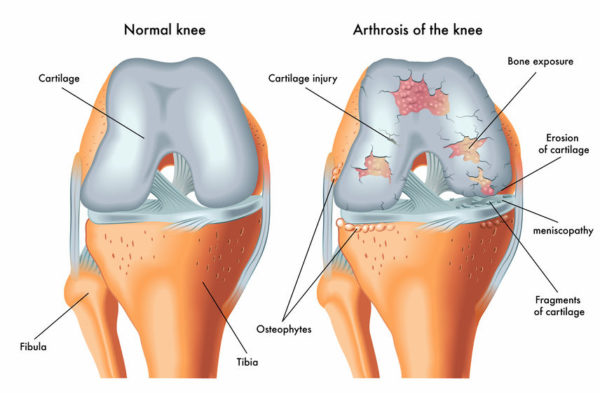
Arthritis (meaning joint inflammation) occurs in joints when the protective cartilage that covers the surfaces where two bones meet, is damaged. There are many different reasons why this might occur but the most common cause is osteoarthritis, thought to be the result of wear and tear that occurs in many of us as we age. Other conditions that lead to arthritis include:
- Inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout
- Damage to the joint surface after an injury (post-traumatic arthritis)
- Damage to the joint as a result of infection (septic arthritis)
When the cartilage is damaged or worn away, the space between the two bones is reduced. An example is between the femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shin bone) in knee arthritis. In severe cases, the bones begin to rub painfully against each other when the joint is moved.
The symptoms of arthritis include pain, swelling of the affected joint and often stiffness, meaning the joint does not move normally. There are many different ways to treat arthritis including lifestyle and activity modification, specialised exercise programs, medications, injections of various types and surgery. Your surgeon can help you decide which treatment is best for you.